- Home
- Secondary
- Subject Information
Design and Technology
BackIntroduction

Welcome to the Design and Technology department at Tabor Academy!
We proudly teach: Resistant Materials, Textiles and Graphic design. This is available for both Key Stage 3 and Key Stage 4.
Our aims and objectives of the Design and Technology Department relate directly to the requirements of The National Curriculum. We see Design and Technology as an area to develop practical and creative skills that aim to prepare young people for life in a changing technological society.
We strongly maintain that a modern approach to teaching in Design and Technology should encompass areas such as: design and communication, mechanisms, structures, health and safety and computer applications alongside the more traditional skills of a realisation in: wood, electronics, metal and plastic. We aim and endeavour to excite and challenge pupils at Tabor Academy, both in lessons and extra-curricular time.
We offer the practical applications of mathematical, scientific and art concepts are combined with practical skills. We develop an understanding of aesthetic, social and environmental issues together with industrial practices. The wider influences of our environment, social and moral choices are naturally woven into the teaching and learning in the classroom and indeed, through all aspects of designing for others. We encourage students to reflect on their work, evaluate present and past design and combine with modern technology alongside its uses and its impact. Technology helps all students to become critical and creative designers who will become informed consumers for the future.
Each course of KS3 Design and Technology at Tabor Academy is designed to further improve the students’ designing and making skills. We recognise the value this through embedding the Personal, Learning and Thinking Skills such as Team Work, Innovation and Creativity in order to be successful. We build upon the students’ knowledge and skills at KS3 and utilise their achievements in order to prepare them for GCSE.
Every student studies Design and Technology for 1 hour per hour a week at KS3.
In KS4 every student will have 3 hours a week and this will be split into: One theory lesson, one skills’ lesson and one practical lesson.
KS3
Each course of KS3 Design and Technology at Tabor Academy is designed to further improve the students’ designing and making skills. We recognise the value this through embedding the Personal, Learning and Thinking Skills such as Team Work, Innovation and Creativity in order to be successful. We build upon the students’ knowledge and skills at KS3 and utilise their achievements in order to prepare them for GCSE.
Every student studies Design and Technology (Graphics, Textiles or Resistant Materials) for 1 hour a week in a rotation with Food Preparation and Nutrition.
Resistant Materials
In Resistant Material lessons, students will learn a variety of skills, including traditional practical workshop skills, marking out skills and gain skills using our machines and facilities. Students will complete a number of projects that will enhance both their practical skills, and theoretical understanding of this wide-ranging subject. The projects will allow students to build on, and develop, their skills enabling them to successfully complete GCSE courses at KS4.
Practical projects will see the use of resistant materials to design and create solutions to a given brief. We aim to produce a product outcome in wood, metal and plastic throughout the course of KS3.
Graphic Design
In Graphic Design, students will learn a variety of skills including skills in Brand development and Logo Design. Students will complete a number of projects that will enhance their practical, theoretical and knowledge of paper and boards. The projects will build on their design skills and use of CAD to create solutions for a design brief.
The projects build on and develop their skills enabling them to successfully complete this at GCSE at KS4.
Practical projects will see them manipulating paper to create pop up cards, develop logos and work on building a brand.
Textiles lessons
In Textiles’ lessons, students will learn a variety of skills, including traditional hand sewing skills, how to use the sewing machine, gain knowledge of surface texture techniques and practicing various dyeing methods. Students will complete a number of projects that will enhance both their practical skills and theoretical understanding of textiles. The projects will allow students to build on and develop their skills enabling them to successfully complete this as a GCSE at KS4.
Practical projects will see the use of fabrics, construction of textile items and exploration of various surface interest. They will research, design and create solutions from a given brief to a final product. We aim to produce product outcomes in fabric such as pencil cases, pillows and bags throughout the course of KS3.
KS3 Projects-Graphics
Year 7-Pop up card
Skills: Researching, design and development, cutting and
manipulating paper. Colour and shading.
Knowledge: Motions and mechanisms, paper and how it is made.
Year 8-Trainer design and packaging
Skills-Research, designing and creating a logo design. Modelling
Packaging.
Knowledge-Nets, packaging, biomimicry.
Year 9- Italian cafe
Skills-Modelling with card, mont board; developing names and
branding.
Knowledge-Photoshop, brand and logo development.
KS3 projects-RM
Year 7-Pencil Holder
Skills: Researching, design and development, tools and equipment
Use.
Knowledge: Basic knowledge of plastics, wood. Health and safety.
Basic understanding of woods and manufactured boards
Year 8-Mechanical Toy
Skills-Research, designing, modelling, creating joints.
Knowledge-Motions, Mechanisms, cams and followers.
Year 9-Steady hand game
Skills-Research and design development. Advance joints and
metal bending.
Knowledge-Electronics, resistors. Metals.
KS3 projects-Textiles
Year 7-Pencil case
Skills: Researching, design and development, sewing machine and
Basic hand skills.
Knowledge: Natural and synthetic fabrics basic knowledge. Health
And safety.
Year 8-Pillow
Skills-Research, designing and developing, surface techniques
Such as tie dye and applique.
Knowledge-Dyeing, applique and fabric paints. Holy level designer.
Year 9-Tote Bag
Skills-Research, design and development, pattern construction
And seams and hems.
Knowledge-Production planning, pattern planning.
ASSESSMENT
All summative assessment within the department is in line with the Design Curriculum Team and the schools’ assessment and recording policy. Key Stage 3 students have a minimum of 6 assessed pieces a year including assessed homework pieces. Students can expect to receive regular advice on their work and its progress from their teacher including frequent verbal feedback, which will be recorded by the student.
Homework expectations
The Design and Technology department follows the Academy policy on homework and it will be set fortnightly. It is essential a disciplined approach towards homework is taken for students to fully meet the course requirements.
Students will have their homework tasks posted onto Google Classroom by their class teacher in addition to the student requirement to record their homework in their homework diaries.
Equipment
Please ensure that your child is equipped for learning. Students must have their pen, pencil, rubber and ruler for class.
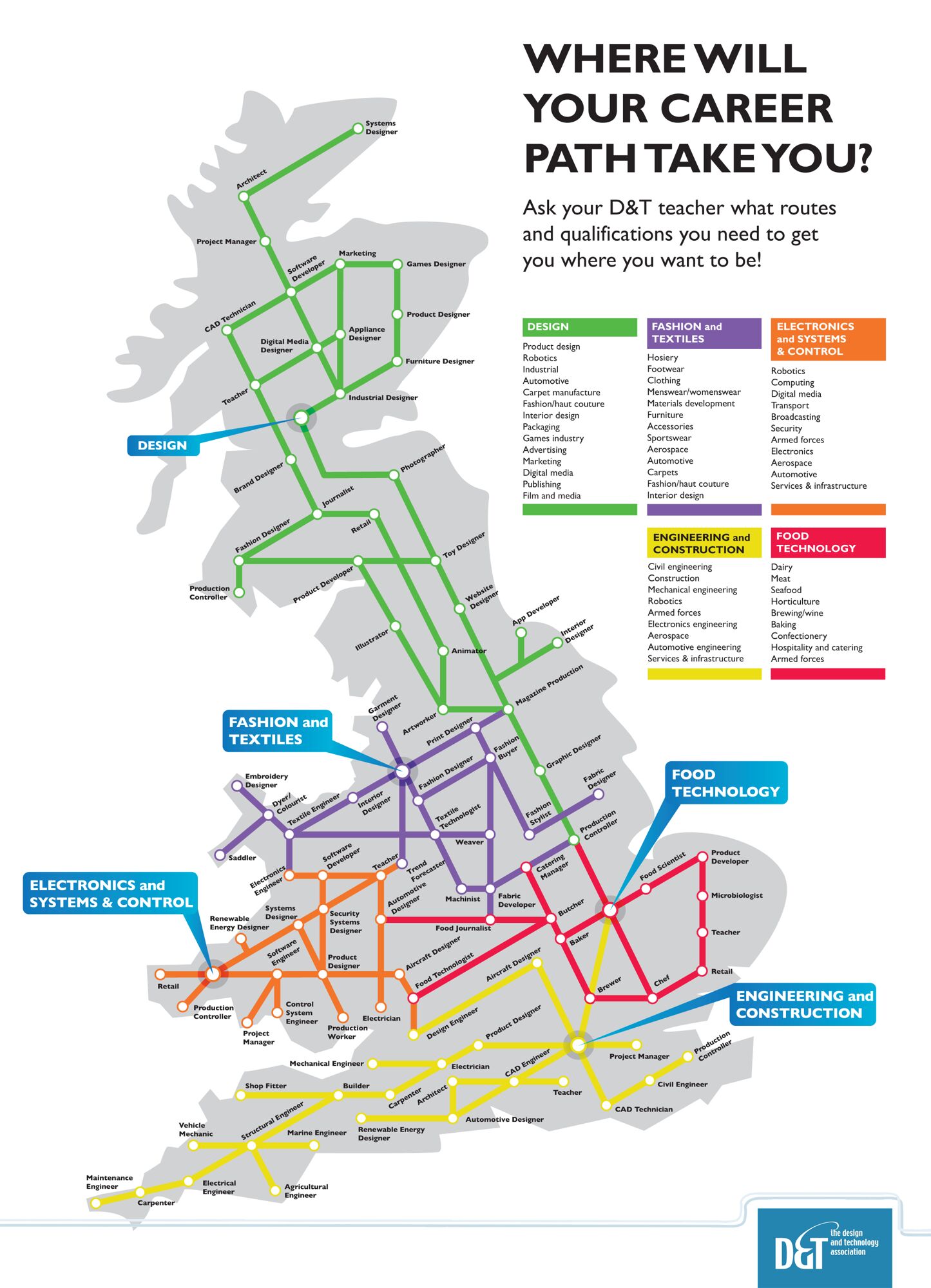
KS4
The GCSE in Design and Technology enables students to understand and apply iterative design processes through which they explore, create and evaluate a range of outcomes. The qualification enables students to use creativity and imagination to design and make prototypes (together with evidence of modelling to develop and prove product concept and function) that solve real and relevant problems, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. It gives students opportunities to apply knowledge from other disciplines, including mathematics, science, art and design, computing, and the humanities.
Students will acquire subject knowledge in design and technology that builds on Key Stage 3, incorporating knowledge and understanding of different materials and manufacturing processes in order to design and make, with confidence, prototypes in response to issues, needs, problems and opportunities.
Students learn how to take design risks, helping them to become resourceful, innovative, and enterprising citizens. They should develop an awareness of practices from the creative, engineering and manufacturing industries. Through the critique of the outcomes of design and technology activity, both historic and present day, students should develop an understanding of its impact on daily life and the wider world and understand that high-quality design and technology is important to the creativity, culture, sustainability, wealth and wellbeing of the nation and the global community.
A final prototype could be a highly finished product, made as proof of concept before manufacture, or working scale models of a system where a full-size product would be impractical.
We offer the following specification: AQA GCSE Design Technology
AQA GCSE-Resistant Materials, Textiles and Graphic Design.
This qualification is linear. Linear means that students will sit all their exams and submit all their non-exam assessment at the end of the course.
Subject content:
- Core technical principles
- Specialist technical principles
- Designing and making principles
Assessments:
Written component
What is assessed:
- Core technical principles
- Specialist technical principles
- Designing and making principles
How it is assessed:
- Written exam: 2 hours
- 100 marks
- 50% of GCSE
Questions:
Section A – Core technical principles (20 marks)
A mixture of multiple choice and short answer questions assessing a breadth of technical knowledge and understanding.
Section B – Specialist technical principles (30 marks)
Several short answer questions (2–5 marks) and one extended response to assess a more in depth knowledge of technical principles.
Section C – Designing and making principles (50 marks)
A mixture of short answer and extended response questions.
2. Non-exam assessment (NEA)
Practical application of:
- Core technical principles
- Specialist technical principles
- Designing and making principles
How it is assessed:
- Non-exam assessment (NEA): 30–35 hours approx.
- 100 marks
- 50% of GCSE
Task(s)
- Substantial design and make task
Assessment criteria:
- Identifying and investigating design possibilities
- Producing a design brief and specification
- Generating design ideas
- Developing design ideas
- Realising design ideas
- Analysing & evaluating
- In the spirit of the iterative design process, the above should be awarded holistically where they take place and not in a linear manner
- Contextual challenges to be released annually by AQA on 1 June in the year prior to the submission of the NEA
- Students will produce a prototype and a portfolio of evidence
- Work will be marked by teachers and moderated by AQA
Curriculum Maps
Extra Curricular
We are pleased to be able to offer lots of clubs to all areas of Design and Technology. These clubs are incredibly popular and students are able to attend an after-school club for Textiles and Graphics and lunch time for resistant materials.
We aim to allow students to develop their skills for pleasure in a more relaxed environment. We also hold special events during the year including a fashion show and ‘Bake Off’ competitions.
Parents can help their children to develop an awareness of the role of Design and Technology in development of the modern world through simple yet effective ways.
- Help your child to see the value of designing and making in today’s modern world, and the good job opportunities that this line of study can offer.
- Encourage your child’s enjoyment in, and to help them in solving, technological problems.
- Give time and opportunities for your child to discuss their technology projects at home and give feedback on the things they make made.
- Encourage your child to complete their homework on time and to the best of their ability.
To encourage your child to always aim to improve on their previous best performance
Useful Links
Links to Websites & Documents
- www.technologystudent.com
- www.design-technology.info/
- www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/
- What is Design & Technology
Possible places to visit to support students learning
The Design Museum
224 - 238 Kensington
High Street
London
W8 6AG
William Morris Gallery, Walthamstow E17
Trips And Events
Y7 LegoLand trip
Y9 &10 Victoria and Albert Museum Trip
Y9 & Y10 Design museum
D and T Wall of Fame at Tabor
Prop Club for the Drama shows afterschool for all Year groups
Textiles Club afterschool for all Year groups
Resistant Material Club at lunch time